Overseas investors' participation in HKEx's futures and options market reached the highest level since 2005, according to Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited’s (HKEx) Derivatives Market Transaction Survey 2011/12. The survey found that Exchange Participants' (EP) principal trading and investor trading continued to contribute equally to HKEx's derivatives market turnover from July 2011 to June 2012 and that overseas investors' contribution marginally surpassed that of local investors for the first time.
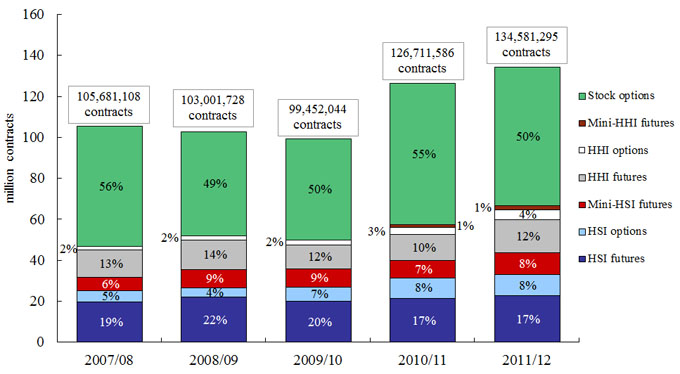
In 2011/12, the total turnover for the futures and options under study was 135 million contracts (referred to as the total market turnover in this survey), up 6 per cent from 127 million contracts in 2010/11. Stock options remained the dominant product by turnover, contributing 50 per cent of the total market turnover (as measured by contract volume) (see Figure 1).
Key findings of the 2011/12 survey
- EP principal trading (comprising market maker trading and EP proprietary trading) contributed 50 per cent of total market turnover (compared with 51 per cent in 2010/11), 69 per cent of stock options turnover (the same as in 2010/11) and 30 per cent of turnover in other futures and options (29 per cent in 2010/11) (see Figure 2).
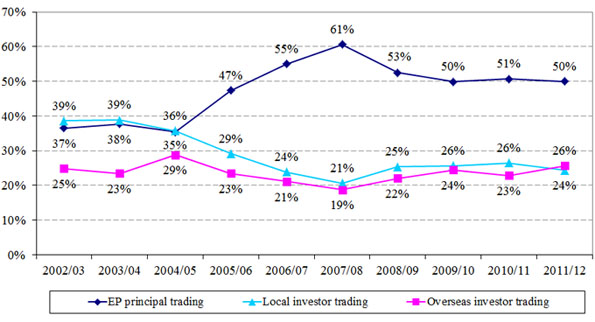
- Overseas investors contributed 26 per cent of total market turnover (up from 23 per cent in 2010/11), and local investors contributed 24 per cent (down from 26 per cent in 2010/11) (see Figure 3).
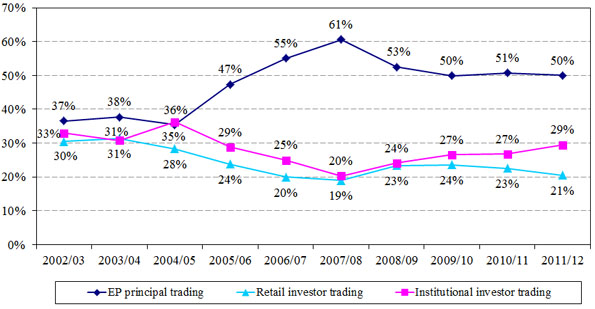
- Retail investors contributed 21 per cent of total market turnover (down from 23 per cent in 2010/11), mostly from local retail investors (17 per cent). Institutional investors contributed 29 per cent in 2011/12 (up from 27 per cent in 2010/11), most of this (22 per cent) being from overseas institutional investors (See Figures 2 and 3).
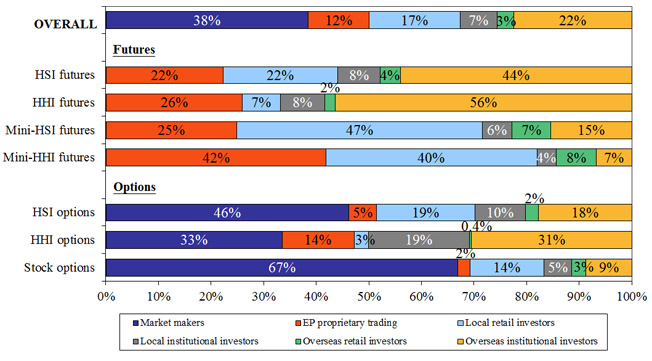
- Major products (see Figure 4):
- For Hang Seng Index (HSI) futures, overseas institutional investors were the major contributors (44 per cent of the product’s turnover), while EP principal trading and local retail investor trading were also significant (22 per cent for each).
- For H-shares Index (HHI) futures, overseas institutional investors were the major contributors (56 per cent). EP principal trading was also significant (26 per cent).
- For Mini-HSI futures, the major contributor was local retail investors (47 per cent), with a significant contribution from EP principal trading (25 per cent).
- For Mini-HHI futures, EP principal trading and local retail investor trading were the most significant (42 per cent and 40 per cent respectively).
- For HSI options, EP principal trading was dominant (51 per cent, 46 per cent from market making), while local investors’ contribution was also significant (28 per cent, 19 per cent from individuals).
- For HHI options, the major contributors were EP principal trading (47 per cent, 33 per cent from market making) and overseas institutional investors (31 per cent).
- For stock options, EP principal trading was dominant (69 per cent, 67 per cent from market making), while local investor trading was also significant (19 per cent, 14 per cent from individuals).
- Among overseas investors, UK investors were the largest contributor to overseas investor trading (28 per cent in 2011/12, up from 25 per cent in 2010/11). They were followed by Continental European investors (24 per cent, up from 16 per cent in 2010/11) and US investors (16 per cent, down from 23 per cent in 2010/11). Almost all trading from these origins came from institutional investors (over 95 per cent). The aggregate contribution from investors in Asia outside Hong Kong was 28 per cent of overseas investor trading, mainly from Mainland China and Singapore (12 per cent and 11 per cent respectively) (see Figure 5).
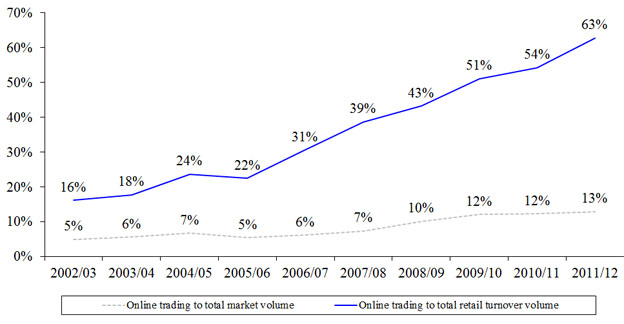
- Retail online trading contributed 63 per cent of total retail investor trading (up from 54 per cent in 2010/11) and 13 per cent of total market turnover (compared with 12 per cent in 2010/11) (see Figure 6).
The survey has been conducted annually since 1994. The latest survey covers HSI futures, HSI options, Mini-HSI futures, HHI futures, HHI options, Mini-HHI futures and stock options. These products together accounted for 99 per cent of the total turnover of the HKEx derivatives market during the study period of the 2011/12 survey. The survey had an overall response rate of 91 per cent and the respondents contributed 98 per cent of the total turnover in products under study during the study period.
The full report on the HKEx Derivatives Market Transaction Survey 2011/12 is available on the HKEx website.
Notes:
- "Market turnover" in the report refers to the total turnover, measured in contracts traded, of the products under study.
- Due to their dominance by contract volume, stock options have a large influence on the trading pattern of the HKEx derivatives market even though they have much smaller notional value than the other futures and options.
- HKEx surveyed Exchange Participants only. Their responses stemmed from their own understanding of their clients. HKEx had no direct access to these clients, nor could it verify their nature.
- The survey is subject to a number of limitations. For example, an Exchange Participant might not know the true origins of all its client orders. The Exchange Participant might classify transactions for a local institution as such when in fact the orders originated overseas and were placed through that local institution, or vice versa. As a result, the findings may deviate somewhat from the true picture.
Figure 1. Contract volume and percentage of total by product under study
(2007/08 – 2011/12)
|
Note:
|
Numbers may not add up to 100 per cent due to rounding.
|
Figure 2. Distribution of derivatives market trading volume by investor type
(Jul 2011 – Jun 2012)
(a) Overall
(b) Stock options
(c) Futures & options (excluding stock options)
| Note: |
(1) |
Exchange Participants' principal trading comprises market maker trading and EP proprietary trading. |
|
(2) |
Numbers may not add up to 100 per cent due to rounding. |
Figure 3. Distribution of derivatives market trading volume by investor type
(2002/03 – 2011/12)
(a) Local vs overseas
(b) Retail vs institutional
|
Note:
|
Numbers may not add up to 100 per cent due to rounding.
|
Figure 4. Distribution of derivatives market trading volume by investor type
for overall market and each product (Jul 2011 – Jun 2012)
| Note: |
(1) |
Market maker trading and EP proprietary trading are components of EP principal trading.
|
|
(2) |
Numbers may not add up to 100 per cent due to rounding. |
Figure 5. Distribution of overseas investor trading volume in derivatives by origin
(Jul 2011 – Jun 2012)
|
#
|
Reported origins in “Rest of Asia” in 2011/12 are India, Indonesia, Macau, Malaysia, Philippines, South Korea and Thailand.
|
|
*
|
Reported origins in “Others” in 2011/12 are Africa, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Canada, Cayman Islands, Cyprus, Liberia, Mauritius, Middle East, New Zealand and Republic of Seychelles.
|
| Note: |
Numbers may not add up to 100% due to rounding.
|
Figure 6. Retail online trading to total derivatives market volume
and retail turnover volume (2002/03 – 2011/12)
Ends