(a) Exchange rate risk
Derivative warrants linked to overseas underlying assets that are denominated, traded and settled in Chinese Renminbi (RMB), Hong Kong dollars (HKD) or US dollars (USD) are eligible for issuance.
Investors trading HKD-denominated derivative warrants with overseas underlying assets may be exposed to an exchange rate risk during the term of the derivative warrants when the price and cash settlement amount of such derivative warrants are converted from a foreign currency in which the overseas underlying asset is priced into HKD. Additionally, investors trading in foreign currency denominated (e.g. USD-denominated) derivative warrants with overseas underlying assets corresponding to derivative warrants trading currency may still be exposed to an exchange rate risk if their primary funding income is in a different currency.
(b) Different trading hours between the underlying exchange on which the overseas underlying assets are traded and the Exchange
If trading in the overseas underlying assets is suspended on the underlying exchange, trading in the derivative warrants will be suspended for a similar period.
The trading hours of the underlying exchange (based on Hong Kong time) are likely to be different from the trading hours of the Exchange. Trading in the overseas underlying assets on the underlying exchange may be suspended during non-trading hours of the Exchange. Such suspension may be lifted, and trading may resume, during non-trading hours of the Exchange.
If trading in the overseas underlying assets on the underlying exchange is suspended, trading in the derivative warrants on the Exchange will not be automatically suspended – in such case, the market price of the derivative warrants may fluctuate significantly until trading in the derivative warrants on the Exchange is suspended. If trading in the overseas underlying assets on the underlying exchange resumes following a suspension, trading in the derivative warrants on the Exchange will not be resumed automatically and you will not be able to trade the derivative warrants until trading in the derivative warrants on the Exchange is resumed.
In addition, the trading price of the overseas underlying assets is calculated and published during the trading hours of the underlying exchange. You should be aware of the time zone difference between Hong Kong and the location in which the underlying exchange is situated in assessing the trading price of the overseas underlying assets. The trading prices of the overseas underlying assets may be volatile in response to the movements on the underlying exchange during which the Exchange is not opened for trading of the derivative warrants.
(c) Less public information about the overseas underlying assets and such information may not be available in English or Chinese
There may be less publicly available information about the overseas underlying assets than those about Hong Kong underlying assets and some of that information may not be available in English or Chinese. If you do not understand any such information, you should obtain independent advice.
(d) Foreign tax implications
Investors trading in derivative warrants with overseas underlying assets may be exposed to various foreign tax implications that could adversely affect their overall investment returns. The foreign tax rules may be intricate, and their applicability can vary based on individual circumstances. You should refer to the listing documents to understand the details of foreign tax implications (if any) and/or consult your tax advisor before investing in such products.
(e) Political and economic risk
The trading prices of the overseas underlying assets may be subject to political, economic, financial and social factors that apply in those geographical regions, which may differ favourably or unfavourably from those factors that apply to Hong Kong. Moreover, foreign economies may also differ favourably or unfavourably from the Hong Kong economy in important respects such as growth of gross national product, rate of inflation, capital reinvestment, resources and self-sufficiency.
(f) Potential differences between derivative warrants denominated in foreign currency and in HKD
i. Differences in spread
Foreign currency-denominated derivative warrants may expose investors to a wider bid-ask spread (in terms of monetary value based on the relevant exchange rate), resulting in higher transaction costs.
Below is an example illustrating the differences in one tick of bid-ask spread between HKD-denominated and USD-denominated derivative warrants.
|
Trading currency
|
Price range (in trading currency unit)
|
1 tick of bid-ask spread
|
|
HKD
|
From HK$0.01 to HK$0.25
|
HK$0.001
|
|
USD
|
From US$0.01 to US$0.25
|
US$0.001 (equivalent to approximately HK$ 0.0078)
|
ii. Differences in minimum trading price and liquidity
Derivative warrants are not tradable on the Exchange if the trading price is below 0.01 unit of trading currency. The minimum trading price of derivative warrants denominated in foreign currency (in terms of monetary value based on the relevant exchange rate) may therefore be different from that of derivative warrants denominated in HKD.
Below is an illustrative example:
|
Trading currency
|
No trading if the trading price is less than:
|
|
HKD
|
HK$0.01
|
|
USD
|
US$0.01 (equivalent to approximately HK$ 0.078)
|
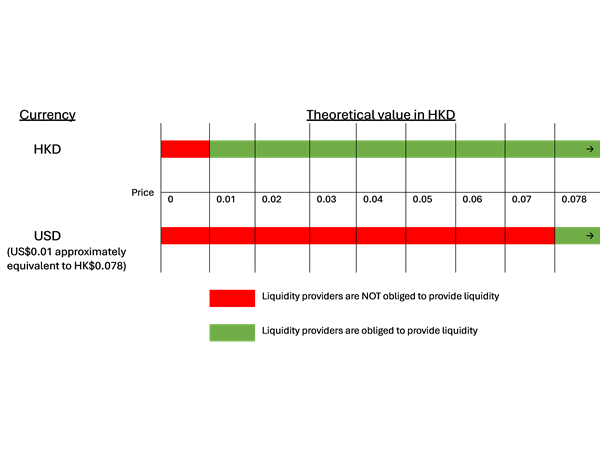
In addition to the minimum trading price, liquidity providers are also not obliged to provide liquidity if the theoretical value of the derivative warrant is less than 0.01 unit of trading currency (see paragraph 3.3(e) of the Industry Principles). Consequently, liquidity in foreign currency denominated derivative warrants may be more limited than that of HKD-denominated derivative warrants.
Below is an illustrative example:
![]()
![]()