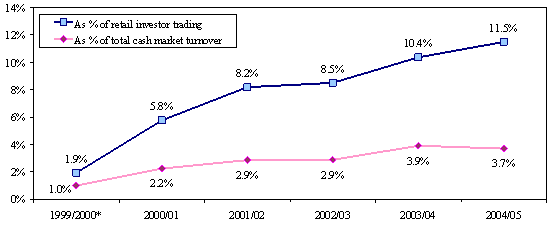
A recent survey by Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited (HKEx) shows that cash market trading gained balanced support from overseas institutional investors, local retail investors and local institutional investors, who contributed 34 per cent, 30 per cent and 27 per cent respectively to market trading in value terms.
The Cash Market Transaction Survey 2004/05 reveals that from October 2004 to September 2005 local investors remained the dominant contributors (56.3 per cent) to the total market turnover in 2004/05, after a similar contribution (56.8 per cent) in 2003/04. Overseas investors, mainly institutional investors, contributed 36 per cent to the total market turnover in 2004/05, the same level as in 2003/04. The remaining 8 per cent was from Stock Exchange Participants’ (EPs) principal trading (trading on the firm’s own account).
Overseas institutional investors made the largest contribution (34 per cent) in 2004/05. The contribution from local retail investors decreased from 34 per cent in 2003/04 to 30 per cent in 2004/05 while that from local institutional investors increased from 22 per cent to 27 per cent. The contribution from overseas retail investors remained small (2 per cent of the market turnover value).
United States (US) investors overtook the United Kingdom (UK) to be the major contributor to overseas investor trading in 2004/05 (29 per cent vs 25 per cent in 2003/04 for the US; 25 per cent vs 28 per cent in 2003/04 for the UK). The rest of Europe was the third most important source (22 per cent vs 24 per cent in 2003/04). The aggregate contribution from Asian origins to overseas investor trading was 18 per cent in 2004/05, slightly down from 20 per cent in 2003/04. Among the Asian origins, Singapore and Mainland China had the largest market shares of overseas investor trading in 2004/05 (8 per cent and 5 per cent respectively).*
Online trading accounted for 11 per cent of retail investor trading, up from 10 per cent in 2003/04 (or 4 per cent of total market turnover, similar to 2003/04).
The Cash Market Transaction Survey has been conducted annually since 1991. For the 2004/05 survey, questionnaires were sent to all 416 Stock Exchange Participants in the target population. The response rate was 91 per cent by number or 97 per cent by turnover value of the target respondents.
The full report on the Cash Market Transaction Survey 2004/05 is available on the HKEx website at:http://www.hkex.com.hk/eng/stat/research/pages/research.aspx.
Figure 1. Distribution of cash market trading value by investor type
(Oct 2004 – Sep 2005)
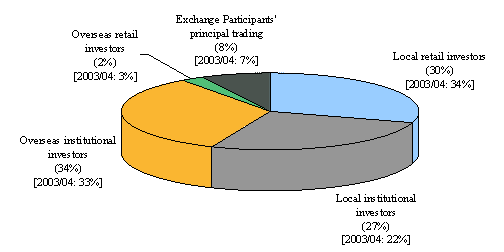
Figure 2. Distribution of overseas investor trading value in cash market by origin
(Oct 2004 – Sep 2005)
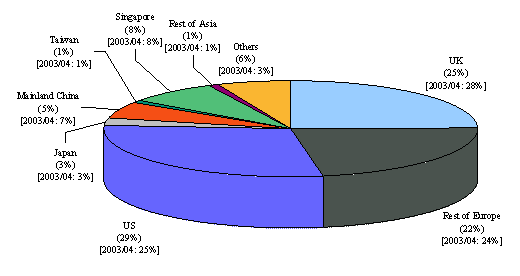
Figure 3. Percentage share of online trading value in cash market
(1999/2000 – 2004/05)